Dividend is the profit that is distributed from a company’s earnings to qualified shareholders. Cash dividend is the most popular form of dividends and it is distributed by firms that make profit. This decision to share a part of the profit with eligible shareholders is taken after a board meeting and approved by shareholders at annual general meeting (AGM). In addition, the company must set aside some percentage of the profit and must be transferred to reserves as per the Companies Act and then the company can decide to share the rest of its earnings.
Companies that pay dividend on its stocks which are owned by its shareholders are known as dividend stocks. Sometimes companies may decide to pay an interim dividend, which is nothing but dividends paid before the end of the financial year and before the annual general meeting of board of directors. Final dividends are those dividends that are paid at the end of the financial year after preparation of financial statement for that financial year, recommendation of Board of directors and shareholders’ approval.
Normally, well established companies like ITC, Infosys, etc. pay dividends regularly. Companies that are in its early stage and high growth companies which are looking for expansion and grabbing market share will most probably skip paying dividends. They prefer to invest their earnings in technology and other processes to improve profitability and sales.
Dividends are always paid on face value of the share and not on the current share price. So if a company announces to pay 10% dividend, this 10% is calculated on the face value. Assume the face value of a company is Rs 10 and a shareholder holds 200 shares, then the shareholder will receive a dividend of Re 1 for each share. So, the amount the shareholder will receive is Rs 200 as the total dividend.
Important Dates
A shareholder must also know some important dates so that he/she can check if they are eligible for the dividends. They are dividend declaration date, record date, ex-dividend date and payment date.
Declaration date: The date on which a company’s annual general meeting takes place and the company’s board announces the dividend issue.
Ex-dividend date: This is the most important date for investors. The ex-dividend date is normally before the record date. Shareholders who buy the stock on or after ex-dividend date are not entitled for any dividend. This is the date on which a shareholders’ eligibility for any dividends will expiry.
Record date: The date on which a company will check its record for shareholder’s eligibility. If the name of the shareholder is not present on the company’s record as on the record date, then the shareholder will not receive any divident or bonus shares.
Payment date: The date on which your account will be credited with the dividend amount for each share. If the dividend is Rs 3 and you hold 200 shares you will receive Rs 600 in your bank account that has been linked with you trading account. This payment date is usually 30 to 45 days after the record date.
The table below shows various dates with respect to BPCL dividend
Declaration date | Ex-dividend date | Record date | Payment date (on or before) |
26-May-21 | 16-Sep-21 | 18-Sep-21 | 02-Nov-21 |
High Dividend Yield Stocks
Majesco is the top dividend yielding stock among all stocks. When it comes to large cap stocks, the top dividend yielding stocks in the last financial year 2021 are Indian Oil, Coal India, Hindustan Petroleum, Indus Towers, Hindustan Zinc, Power Grid Corp, ITC, Petronet, NMDC, Bharat Petroleum, Ambuja Cements. As we can see from the list, most of the companies’ shares are related to public sector enterprises. So we can say that to build a portfolio of dividend stocks so that an investor receives good dividend income, it is better to focus on public sector companies and well established companies like Nestle, HDFC AMC, ITC, JSW Steel, etc.
Dividend Ratio
There are two important ratios a shareholder must know. they are dividend payout ratio and dividend yield.
Dividend payout ratio is the total annual dividend paid per share for a financial year divided by earnings per share for that financial year.
Dividend yield is the Annual dividend per share divided by current share price.
Hence, from the above two formulae we can infer that the only difference while calculating dividend payout and dividend yield is the denominator.
Generally, if a company pays good dividend, the scope for capital appreciation or increase in its share price is less.
Where to check dividend information in NSE website
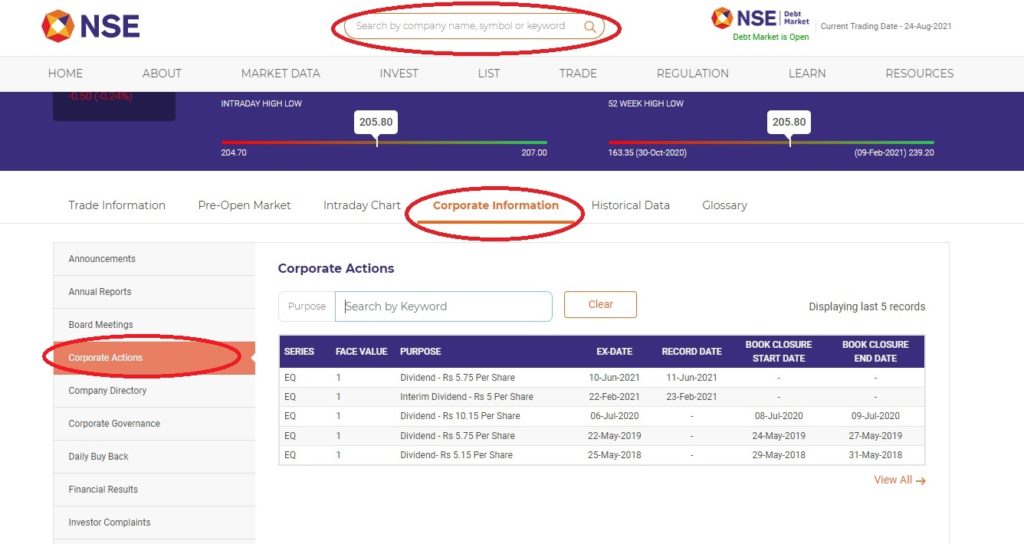
To know more about top dividend yielding stocks, click here